Contact Information
Phone:86 010-51284966
Phone:86 18518110097
E-mail:bjsbl_sale@163.com
Address: Room 403, Building B, Xinhua International Center, Huaxiang, Fengtai District, Beijing
7.4 magnitude earthquake in Maduo County, Qinghai Province
2021-05-25
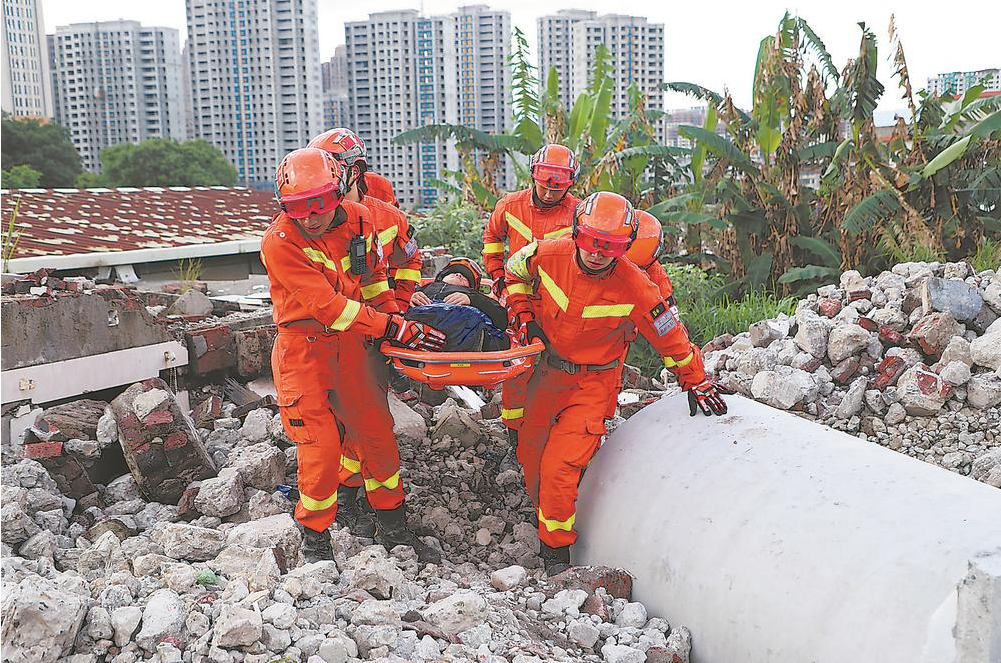
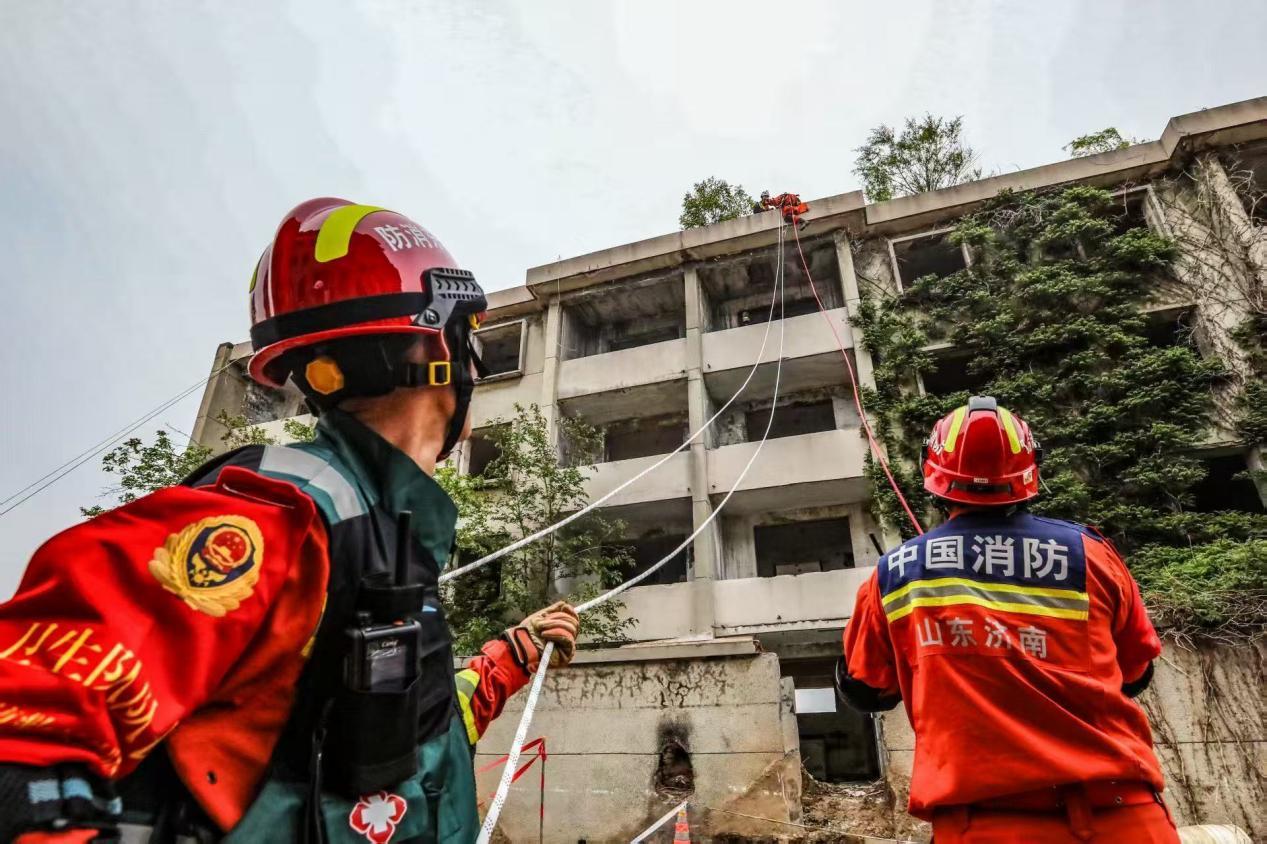
At 2:04 AM on May 22, a 7.4 magnitude earthquake struck Maduo County in Golog Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province. This is the strongest earthquake in China since the Wenchuan earthquake in 2008. Two expressway bridges have collapsed, and national and provincial highways have been severely damaged, deformed, and uplifted.
Currently, the Yemaotan No. 2 Bridge on the Yu-Gong Expressway and the Changma Bridge on the Hua-Jiu Expressway have collapsed, and national and provincial highways have been severely damaged, deformed, and uplifted. Repairs are underway. The Yu-Gong Expressway and Hua-Jiu Expressway are temporarily closed, and the Qinghai Provincial Department of Transportation has activated its emergency response plan. The main power lines are operating normally, with repairs underway for localized damage.
It is understood that the epicenter of the earthquake is 7 kilometers from the Huanghe Township government, 38 kilometers from Maduo County, 175 kilometers from the Golog Prefecture government, and 385 kilometers from Xining City. The earthquake was widely felt throughout the province, with strong shaking felt in Xining. According to the Golog Prefecture Earthquake Bureau, the shaking was strong in Maduo County, Huashixia Town, and Huanghe Township, with some walls collapsing. No reports of casualties have been received yet.
After an emergency consultation by experts, it has been determined that the Maduo earthquake is a mainshock-aftershock type, with aftershock activity around magnitude 6. As of 4:35 AM on May 22, a total of 104 aftershocks have been recorded, including 40 aftershocks of magnitude 3 or greater, 4 aftershocks of magnitude 4 or greater, and the largest being 4.6 magnitude.